
 Successful maiden flight, six satellites in one launch vehicle! Maximum capacity! Uncover the secret of the “Kinetica-1” launch vehicle
Successful maiden flight, six satellites in one launch vehicle! Maximum capacity! Uncover the secret of the “Kinetica-1” launch vehicle
2020.07.27
“
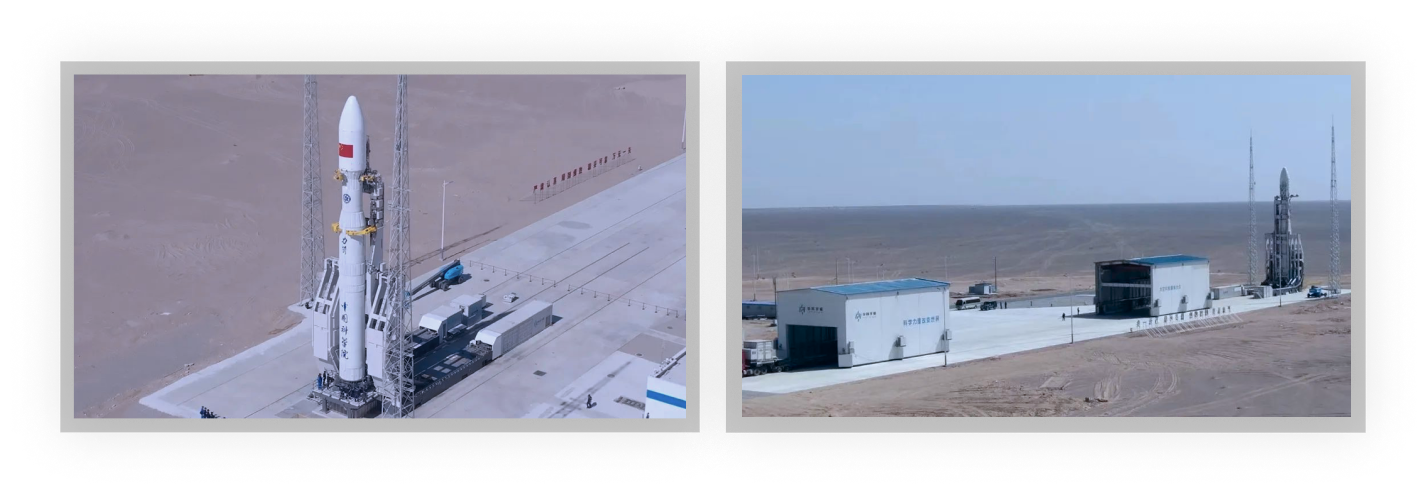
At 12:12 on July 27, 2022, the “Kinetica-1” launch vehicle successfully placed six satellites into predetermined orbits at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center by means of “six satellites in one launch vehicle”, making the maiden flight a complete success. “Kinetica-1” is the largest solid launch vehicle in China, with a maximum launch capacity of 1,500 kg in a 500 km Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO), and was developed by and proprietary to CAS Space.
Overview of Kinetica-1
“Kinetica-1” is a medium-sized solid-propellent launch vehicle, mainly used for small and medium-sized spacecraft launch missions in sun-synchronous orbit and low earth orbit, supporting single-satellite launch, multi-satellites launch (ridesharing or piggyback), rapid constellation networking and network replenishment. It has a dedicated launch station at Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center No. 130 site, and the station has a mobile environmental protection device which features fast response, flexible use, efficient launch, batch storage, and rolling backup.
The “Kinetica-1” adopts a four-stage solid engine tandem layout plan, with a takeoff weight of about 135 t, an overall length of about 30 m, a maximum rocket body diameter of 2.65 m, and a maximum launch capacity of 1,500 kg in 500 km Sun-Synchronous Orbit (SSO).
The rocket is launched in “Horizontal docking, horizontal testing, horizontal transport, vertical launch after overall vertical erection” mode, with the payload and the fairing assembled in the payload technical facilities, followed by turning the payload-fairing composite assembly into a horizontal state, transporting the whole horizontally to the vehicle technical facilities, and mating it horizontally; the logistical transportation vehicle loads the whole vehicle, transports it horizontally to the launch area, tests it horizontally in the launch area, and then launches it after the whole erection.

The development of Kinetica-1 lasted 1,303 days, with 151 items of 761 ground tests, 277,300 lines of code written, 646 drawings made, and more than 850 project documents written. It broke through 6 major key technologies: overall optimized design and test of the large-tonnage solid launcher, advanced power system and vector control, centralized-distributed modern aerospace electronics, low-cost rocket body structure and separation, intelligent flight control, ground use of large-tonnage solid rocket and thermal launch, and the matching of interfaces between various systems, the rationality of various technical processes, the accuracy of force/thermal environmental conditions formulation and the environmental adaptability of the products on the vehicle and the validity of the vehicle technical plan of the engineering was fully assessed and verified.
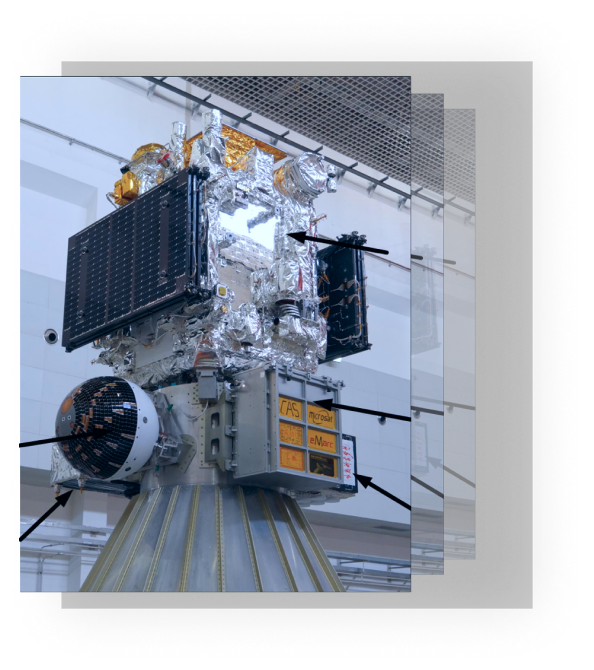
The six satellites carried on the maiden flight of Kinetica-1 are the New Space Technology Test Satellite (621.87 kg), the Orbital Atmospheric Density Detection Test Satellite (41.54 kg), the Low Orbit Quantum Key Distribution Test Satellite (94.3 kg) and the Electromagnetic Assembly Test Double Satellites (95.41 kg) from the Innovation Academy for Microsatellites of Chinese Academy of Science, and the Nanyue Science Satellite (45.86 kg) developed by Shanghai SastSpace Technology Co., Ltd. The maiden flight has a total payload of 1,068.63 kg, with a total satellite mass of 899 kg.
The New Space Technology Test Satellite proposes a “universal satellite platform + open payload module” carrying an extreme ultraviolet imager, wide-field-of-view lobster eye camera, green high-energy HAN-based unit liquid-fuel propulsion system, non-toxic gelation HAN propulsion system, multi-core intelligent processing unit, and other payloads; the main mission objective is to carry out space exploration new technology validation, including space astronomical observations of the solar transition region, space high-energy burst events, X-ray transient sources, and precision measurements of the geomagnetic field.
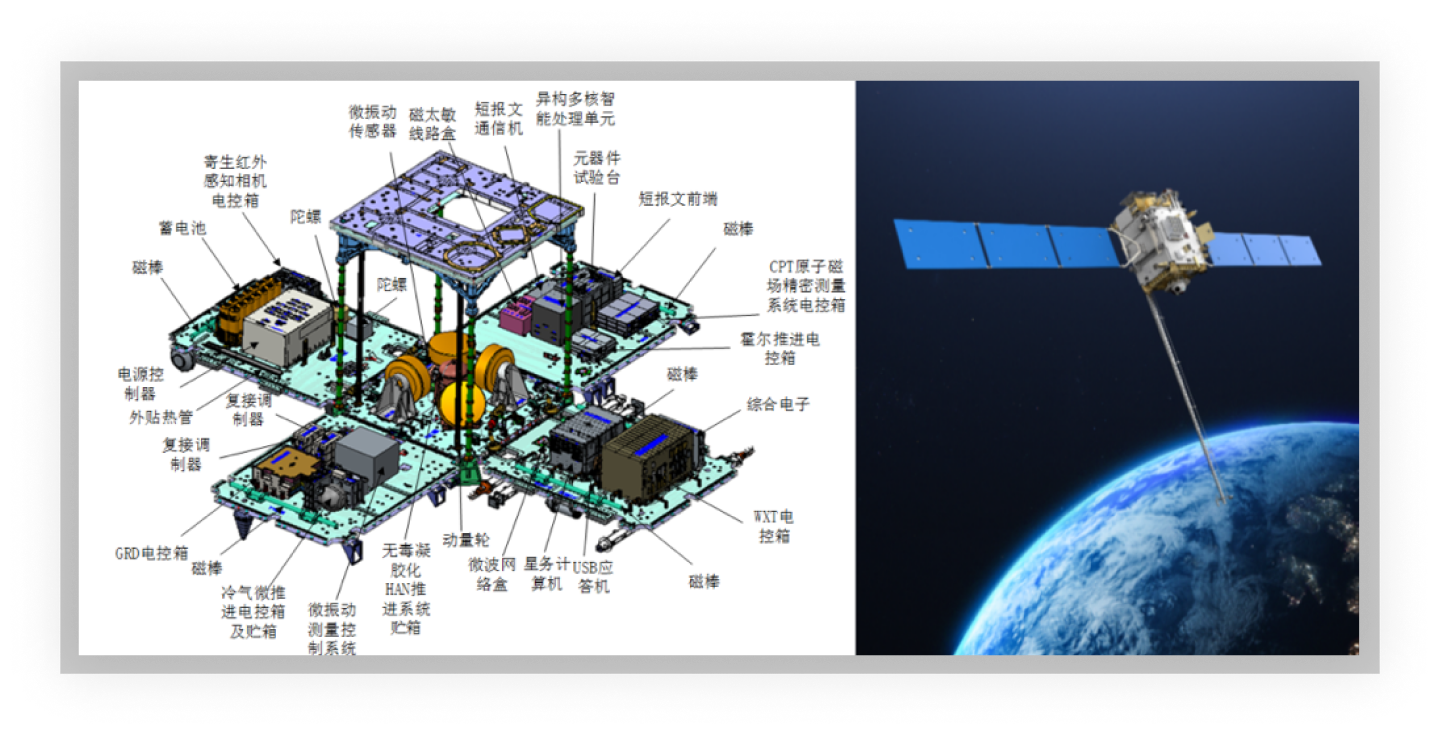
OASDS is a scientific experiment satellite for thermosphere atmospheric density exploration, which uses GNSS data and ground-based orbit determination data from angular reflectors to analyze orbital variations caused by atmospheric drag and invert to obtain accurate thermosphere atmospheric density so as to gradually establish a high-precision atmospheric model and meet the needs of low orbiting spacecraft for high-precision orbital atmospheric model applications.
LEQDS is a micro-nano quantum communication test satellite to carry out in-orbit testing and verification of satellite-ground quantum key distribution technology and applications, with a view to accelerating the construction of an integrated satellite-ground quantum communication network.
The Electromagnetic Assembly Test Double Satellites carried out the electromagnetic force constrained cubic satellite in orbit close separation and docking test, verified the inter-satellite electromagnetic force law of function, and the coupling with the satellite control force for the first time, and at the same time configured the imaging payload to achieve remote sensing imaging to the ground, for the subsequent development of spacecraft distributed reconfigurable technology, and space non-contact role in laying the foundation.
Nanyue Science Satellite belongs to the Haite - 2 constellation (HT-2 constellation for short). The main payload is the Global Navigation Satellite Launch System sea and land environmental detection payload, using BD, GPS, and other GNSS satellites as the launch source, using space-based platforms to receive and process the reflected signals from the Earth’s surface in order to achieve a comprehensive detection of the environmental elements of ocean and land water resources.

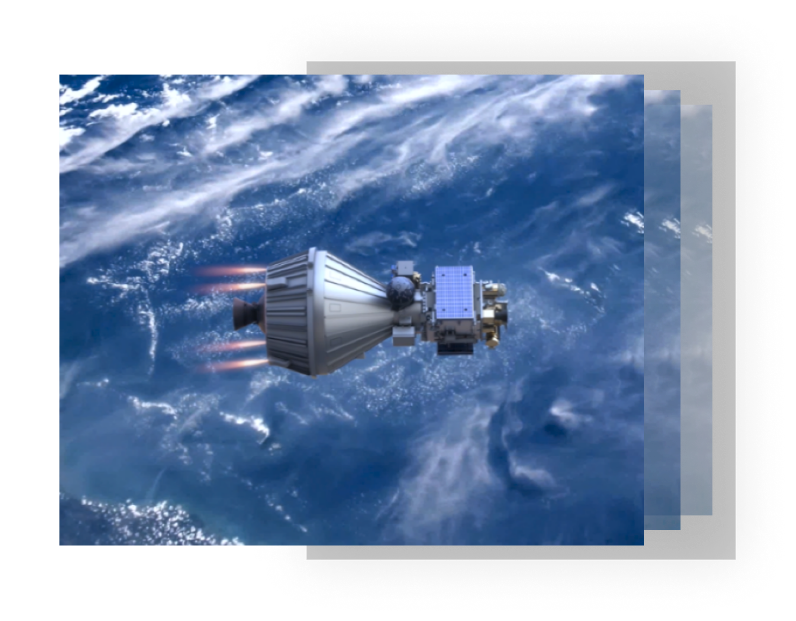
During the flight, the solid-propellent engines at all stages worked nominally. The servo-tracking commands at all stages, the inter-stage separation, the fairing separation, and the payload separation, were nominal. All satellites completed the rate damping, sail deployment, and on-orbit testing nominally post-separation. The preliminary results are interpreted as follows:
(1) The operational performance of solid-propellent engines at all stages has less deviation from the predicted results and meets the requirements.
(2) Stage I, II, and fairing wreckage were in the vicinity of the predicted landing point, and there was no damage to personnel or property.
(3) The angular velocity of satellite separation attitude was recorded as: 0.2°/s before the separation of satellite A, and 0.6°/s before the separation of other satellites.
(5) Accuracy of orbit insertion was recorded as the deviation of the semi-major axis is 545 m, deviation of eccentricity is 1×10-6, and deviation of orbit inclination is 0.0005°.
Technological Innovation
(1) Overall optimized design of the largest domestic launch vehicle
The innovative adoption of single-engine oriented multi-specialty collaborative design and the global optimization of each system plan has significantly improved the comprehensive performance of the rocket with a launch factor of 1.12%.
(2) The first large-tonnage rocket body horizontal modal test in China
The innovative use of a real propellant engine horizontal state, with the air spring multi-point support state, significantly shortens the test cycle, lowers the logistical requirement, and reduces development costs.
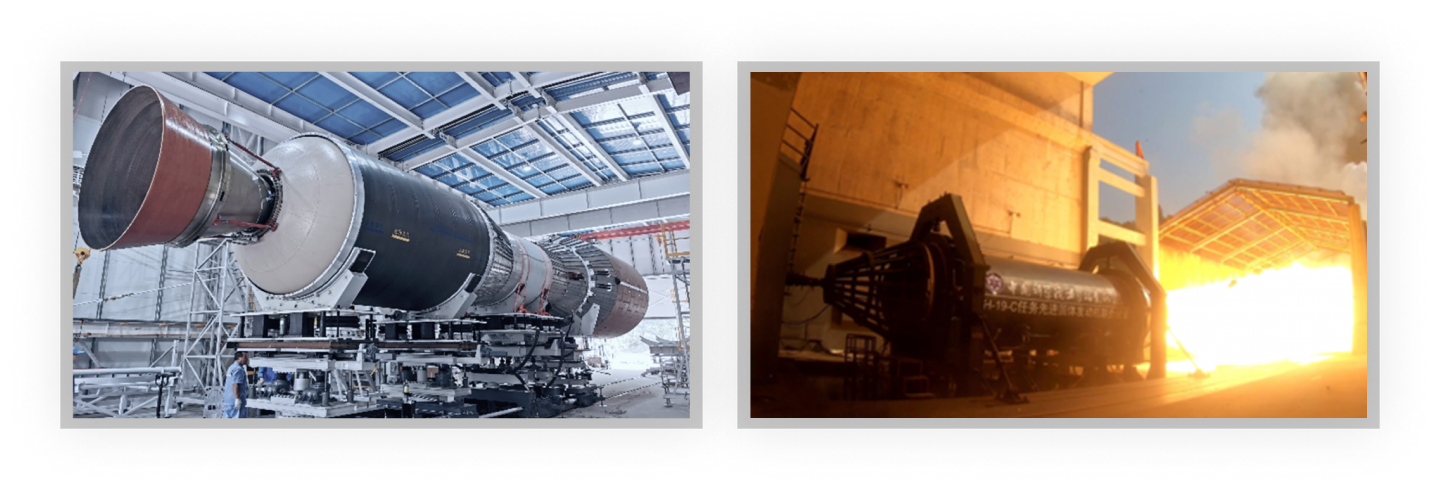
(4) The first domestic heterogeneous structure solid-propellent engine
The vehicle has overcome the core technologies such as PBO fiber spherical winding and front center of oscillation of flexible oscillating nozzle technology, and the engine mass ratio has reached 0.91, which is the largest of the same scale domestically.
(5) The first domestic TT&C fusion using novel avionics system architecture
The vehicle adopts the concept of “single-unit functionalization, functions modularized, and modules generalized”. Custom communication protocols connect modular circuit boards to form hardware generalization and software definition capability.
(6) The first domestic data-driven ground test, launch, and control system software
The design separates software and data; procedures are driven by data; And the test, launch process, and control interface are driven by self-defined data. The number of equipment on the vehicle and on the ground is significantly reduced, and the software-defined rocket design is taking shape.
(7) The first domestic pollution-free energy separation device with large separating force
The design carries out the development of the first domestic large separating force, pollution-free cold gas thrusting separation device. A new form of detectable separation energy is developed in the country.
(8) The first domestic low-cost solid-liquid hybrid structure
The solid engine is combined with the structural part of the stringer skin for the first time in China, and the unified design of the frame-truss of different functional and load-bearing parts, the unified design of the point connection unlocking of different structural surfaces, and the unified design of the tooling frame are completed to achieve the goal of low cost and rapid manufacturing.
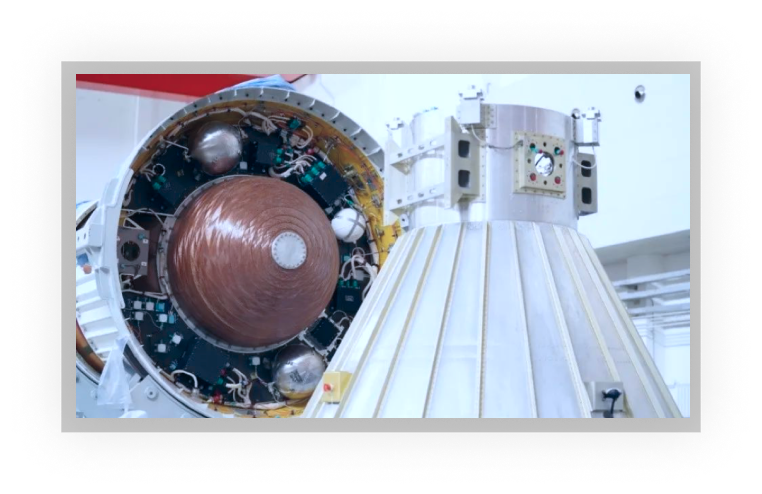
(9) The first domestic triple redundancy CPU software under a 5 ms control cycle
The vehicle adopts a triple redundancy CPU with a 5 ms control cycle and optimizes the calculation and synchronization times. In addition, it takes into account the high-precision and high-reliability requirements of rocket flight.
(10) The first domestic layered architecture flight control system
The embedded integrated flight control software is divided into three layers: functional layer, communication layer, and driver layer; the flight control algorithm is optimized; the large aftereffect residual thrust is used for more accurate orbit insertion correction, and adaptive variable thrust gain is used in the descent phase for attitude control. As a result, it achieves high precision of orbit insertion within 100 meters and stable attitude control throughout the process.
(11) The first domestic mobile multi-functional environmentally secured plant can be assembled
The plant provides complete environmental protection for the vehicle and launch pad for long-term storage, meeting environmental restrictions and significantly saving ground protection equipment costs.
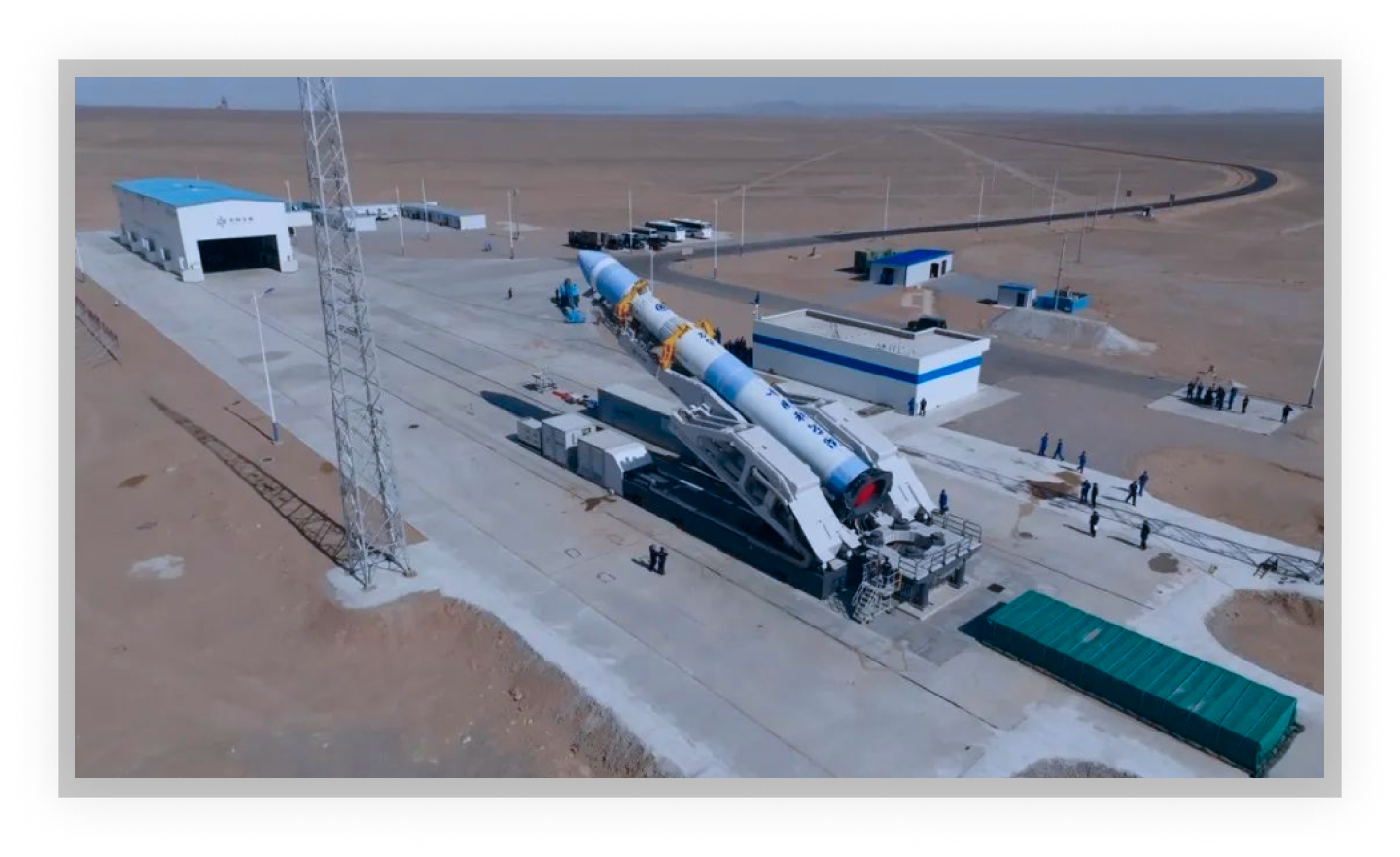
(12) The largest domestic vehicle erection vehicle
The vehicle broke through the design and procedures of the loading synchronization for erection and successfully completed the task of erecting the 135 t launch vehicle.
(13) The largest domestic hot-launch solid-propellent technology
The vehicle adopts the design of single-sided diversion trenches to guide the gas flow. The assessment and verification measures confirmed the design, and the thermal protection design proved effective, reducing launch maintenance costs.
Desgin Model Innovation
(1)
CAS Space develops innovative, advanced, and economical launch vehicles with “engineering science” as the guiding principle. The principle provides a closed-loop platform for integrating various disciplinary innovations into engineering. We devote ourselves to promoting change and innovation for the development models and space science development as a discipline.
(2) Component-oriented optimization for overall integration
The traditional system-subsystem-component development process is optimized into a rapid iterative development mode of component-oriented process, realizing the transformation from “local optimization” of the particular specialty of each system to “global optimization” of the overall system design.
The “Project Collaborative Design Platform” is set up for the first time to dilute and void the concept of subsystems to carry out multi-specialty collaborative design for components, creating conditions for the development of professional integration and the adoption of novel technologies and achieving a competitive load factor of 1.12%.
(3) Quality management model of the lean economy
We adopt a lean economy model to reduce costs from design, production, manufacturing and operation, including
Cost reduction from design: emphasizing systematic optimization to improve comprehensive performance;
Cost reduction from production: adopting unified, universal, and product-oriented design; establishment of an open and modern market supply chain for suppliers in the society;
Cost reduction from manufacturing: building open and information-oriented whole-life-cycle quality management system to reduce process control costs;
Cost reduction from the operational model: setting up technical standards, operational process and evaluation methods for low logistical requirements, and rapid launch cadence to reduce operational costs.
Note: The Lijian series is also known as “Kinetica”, and designations of “PR” or “ ZK” have been used in various literature.